RAM vs. Storage: Don’t Buy the Wrong Mini PC Specs
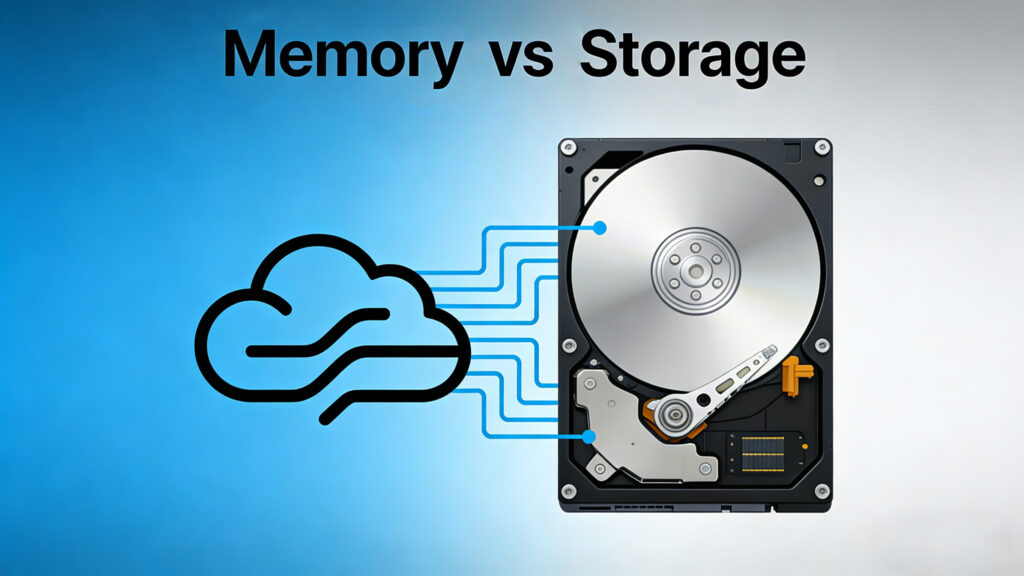
RAM vs. Storage: Don’t Buy the Wrong Mini PC Specs Announcements Buyer Guide Comprehensive Tips Occasion Product Review Q&A Tutorials When shopping for a Mini PC, do you often feel confused by the numbers? You see “8GB RAM” and “512GB SSD Storage.” They both look like “capacity” measured in Gigabytes, but they do completely different things. Many people mistake one for the other. The result? Choosing the wrong combination can lead to a computer that freezes constantly or runs out of space in a month. Today, we will clear up the confusion in the simplest way possible. By the end of this guide, you will know exactly what specs to look for to get the perfect Mini PC for your needs. The Core Concepts: The Chef and The Kitchen To understand the difference, let’s imagine your Mini PC is a Professional Kitchen. 1. RAM (Random Access Memory) The Analogy: RAM is the Chef’s Countertop (Workstation). How it works: This is where the chef (your CPU) actually does the work. When you open a program, it’s like putting ingredients on the countertop to chop and mix. Why size matters: If your countertop is huge (High RAM), the chef can prepare a salad, a steak, and a dessert all at the same time without running out of space. If the countertop is tiny, the chef has to constantly clean up one task before starting another, which slows everything down. Key Feature: It is super fast, but volatile. When you turn off the lights (shut down the PC), the countertop is wiped clean. 2. Storage (Drive/SSD) The Analogy: Storage is the Pantry and Fridge. How it works: This is where you keep all your ingredients permanently. Your Windows operating system, installed software, family photos, and movies live here. Why size matters: A larger pantry means you can stock more food. It doesn’t make the cooking faster, but it ensures you have space to keep everything you buy. Key Feature: It is non-volatile. Even if the power goes out, the food in the pantry stays there safe and sound. Note: Most modern Mini PCs use SSDs (Solid State Drives), which are much faster than the old spinning HDDs. Quick Comparison: At a Glance Here is the breakdown of the technical differences: Feature RAM (Memory) Storage (SSD/Drive) Role Temporary Workspace Permanent Warehouse Analogy Countertop Pantry Speed Extremely Fast Slower than RAM (but SSDs are fast) Capacity Small (e.g., 8GB – 64GB) Large (e.g., 256GB – 2TB+) Permanence Data lost when power off Data saved forever Impact System smoothness & Multitasking How many files/apps you can keep What Does This Mean for Your Mini PC? Understanding the bottleneck is crucial. If your system lacks RAM, the computer is forced to use the slower SSD as temporary memory (paging), causing significant lag. Conversely, if storage is insufficient, you cannot save new data, but system performance may remain stable until the drive is completely full. Here is how to choose based on how you use the computer: For Basic Office & Online Classes: Recommendation: 8GB RAM + 256GB SSD Verdict: The budget-friendly choice. Perfect for browsing, Word documents, and Zoom calls. For Efficiency & Light Creation: Recommendation: 16GB RAM + 512GB SSD Verdict: The standard for 2024. Great for keeping 20+ Chrome tabs open, Photoshop work, and light multitasking. For Pros, Programmers & Designers: Recommendation: 32GB+ RAM + 1TB NVMe SSD Verdict: A large “countertop” for heavy tools. Essential for video editing, compiling code, or running virtual machines. For Home Theater & Media Centers: Recommendation: 16GB RAM + 2TB Storage Verdict: You don’t need massive RAM, but you need a huge “Pantry” to store 4K movies and show collections. Special Advice for Mini PC Buyers Mini PCs are famous for being compact, but this size comes with a rule: Check the upgradeability. Unlike large desktop towers, some Mini PCs have soldered RAM (meaning you cannot change it later). Pro Tip: Always prioritize getting enough RAM upfront. You can usually add an external hard drive for more Storage later, but if your RAM is soldered and too small, you might need to buy a whole new computer. Tech Check: Look for “Dual Channel” memory support for better speed, and ensure the SSD is “NVMe PCIe” for the fastest load times. Conclusion To summarize: RAM is for Speed (Multitasking), and Storage is for Capacity (Holding Files). Now that you understand the specs, you can look at our product list with confidence. We offer a variety of configurations tailored to your specific workflow. If you are still unsure, contact our support team, and we will help you build the perfect setup! HYSTOU HYSTOU has established its R&D headquarters in Shenzhen, drawing on over a decade of experience. Our core team members, who previously served at renowned companies such as Inventec and Quanta Computer, form the backbone of our technical expertise. With robust R&D and innovation capabilities, we remain steadfast in our commitment to pursuing excellence in the field of technology products. Facebook Twitter Youtube Tumblr
RAM vs. Storage: Don’t Buy the Wrong Mini PC Specs Read More »