The Industrial Backbone: Why an RS232 Mini PC is Essential for Legacy Equipment Integration?

Introduction
In the sleek world of modern consumer tech, ports like USB-C and Thunderbolt dominate. Yet, the backbone of global manufacturing—the RS232 serial protocol—remains untouched by time. From automotive assembly lines in Detroit to textile factories in Southeast Asia, the 9-pin COM port is still king.
However, connecting these robust legacy machines to modern IT infrastructure presents a unique challenge. Standard desktops have abandoned serial ports, and dongles are notoriously unreliable. Enter the RS232 Mini PC: the purpose-built bridge between the past’s reliable hardware and the future’s data capabilities.
The "Rigid Demand": Why RS232 Won't Die
The Hidden Risks of USB-to-Serial Adapters
- Data Drift: In high-speed CNC operations, a slight delay in signal timing caused by USB conversion can ruin a precision cut.
- Driver Nightmares: A Windows update can frequently render third-party USB dongle drivers obsolete overnight, stopping production lines.
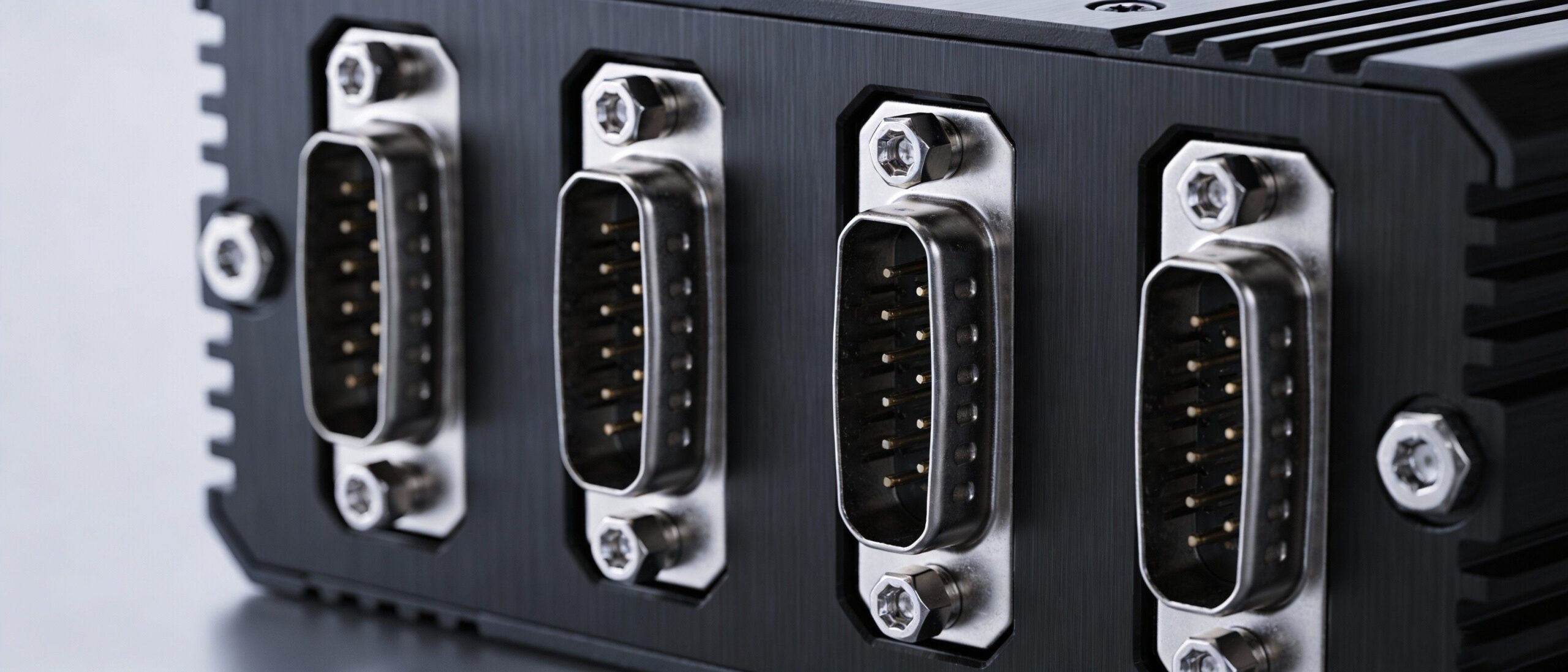
- Physical Connection: USB plugs are designed for easy removal; they vibrate loose easily in industrial settings. DB9 connectors on a Mini PC feature screw locks, ensuring a vibration-proof connection.

Technical Deep Dive: Native Support and Voltage Control
- Super I/O Chip Integration: The COM ports are managed directly by the motherboard’s Super I/O controller, ensuring direct memory access (DMA) and fixed IRQ addresses. This guarantees real-time data processing.
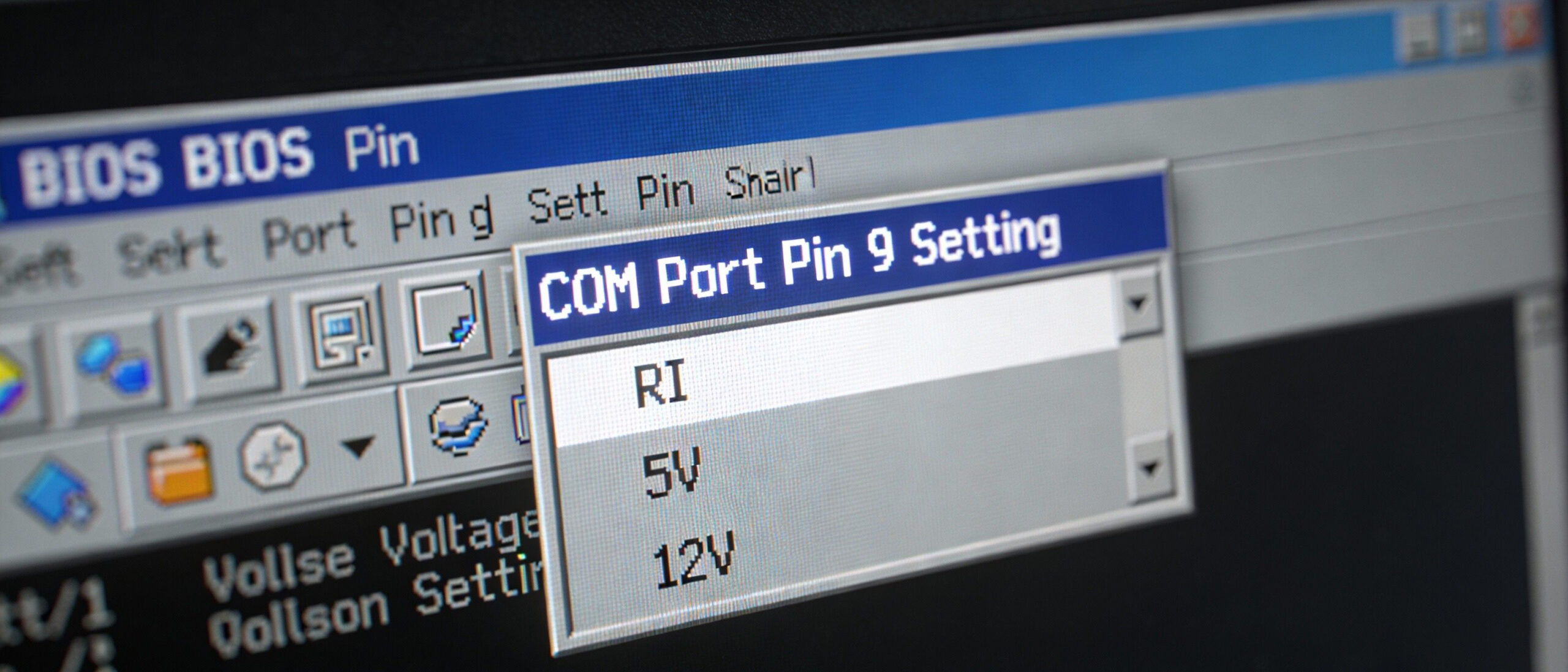
- Pin 9 Voltage Selection: Many modern industrial Mini PCs allow users to configure Pin 9 via BIOS or jumper settings to output 5V or 12V. This is crucial for POS systems (powering customer displays) or barcode scanners, eliminating the need for extra power bricks.
Built for the Factory Floor: Hardware Resilience
- Fanless Design: Moving parts are the first to fail. Fanless Mini PCs use heat sinks to dissipate heat, making them impervious to conductive dust, oil mist, and metal shavings.
- Wide Temperature Range: Unlike an office PC that struggles above 30°C, industrial units can operate from -20°C to 70°C, making them suitable for unconditioned warehouses or outdoor enclosures.
Key Industry Applications
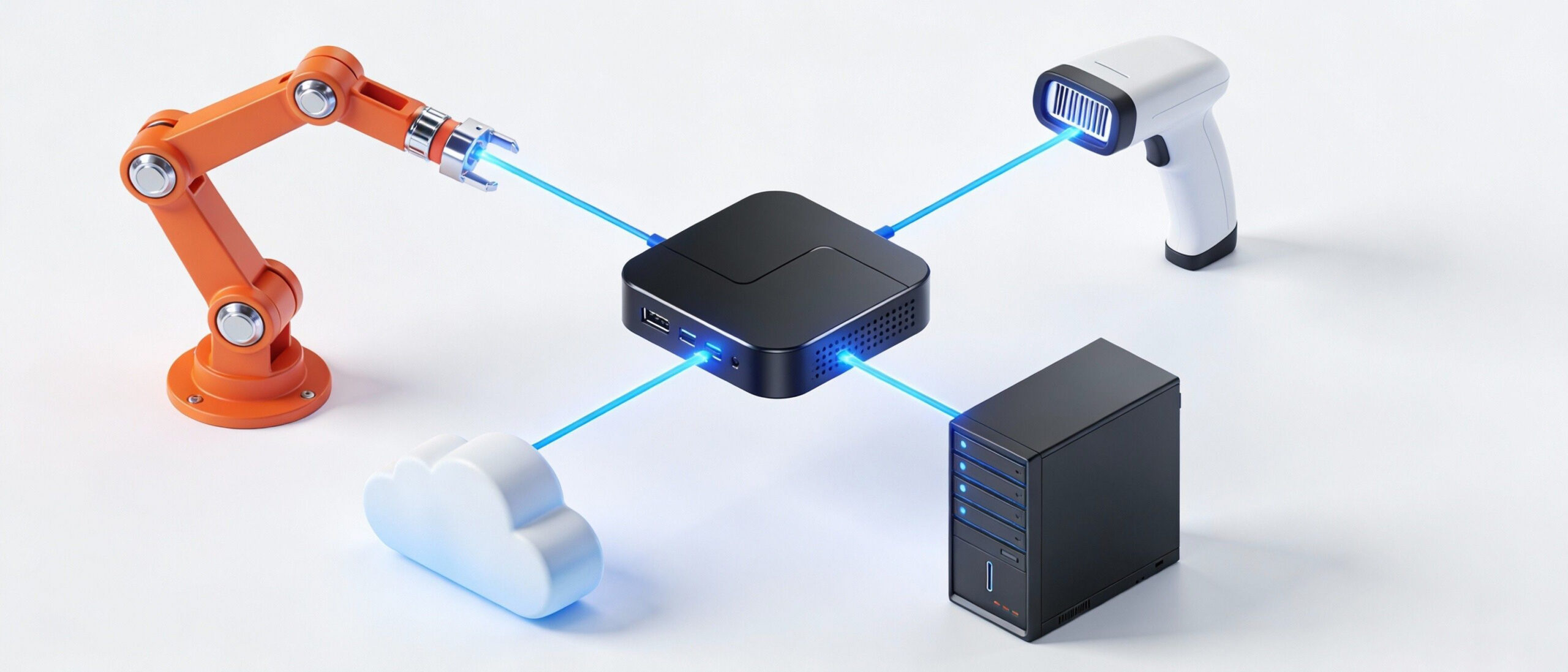
Operators use RS232 Mini PCs to drip-feed G-Code to older CNC mills that lack Ethernet ports. The stability of the PC prevents buffer underruns, which could break expensive tooling.
Blood analyzers and older MRI machines often output data via serial streams. A Mini PC collects this data, parses it, and sends it to the hospital’s central EMR system via LAN or Wi-Fi.
Self-service kiosks use COM ports to connect reliable legacy peripherals: cash dispensers, receipt printers, and card readers.

How to Choose the Right Model
- Port Count: Do you need RS232, or also RS422/RS485 for long-distance transmission?
- Isolation: For electrically noisy environments, look for “Isolated COM Ports” to prevent power surges from frying the motherboard.
- Expansion: Does it have a Mini-PCIe or M.2 slot for 4G/5G modules to transmit the serial data remotely?

HYSTOU
HYSTOU has established its R&D headquarters in Shenzhen, drawing on over a decade of experience. Our core team members, who previously served at renowned companies such as Inventec and Quanta Computer, form the backbone of our technical expertise. With robust R&D and innovation capabilities, we remain steadfast in our commitment to pursuing excellence in the field of technology products.





