Top 5 Industrial Computing Hardware Trends Defining 2026

The Shift from “Smart” to “Autonomous”
We have officially entered 2026, and the landscape of industrial automation is no longer just about connecting devices—it is about enabling them to think. For system integrators and manufacturing CTOs, the hardware deployed on the factory floor this year faces a new set of demands. It is not enough to simply survive harsh environments; today’s Industrial PCs (IPCs) must process complex AI models locally and communicate at speeds previously reserved for data centers.
Based on the latest silicon roadmaps and market shifts, here are the five critical trends in industrial computing hardware that are dominating 2026.
1. The NPU Revolution: Edge AI Goes Native

For years, running AI at the edge meant bulky setups with power-hungry discrete GPUs. That era is ending. The most significant hardware shift in 2026 is the standardization of the Neural Processing Unit (NPU) directly within the CPU die.
Processors like Intel’s Core Ultra series and advanced ARM-based SoCs now integrate dedicated AI acceleration engines. This architecture allows compact, fanless industrial computers to execute machine vision, optical inspection, and predictive maintenance workloads efficiently.
- Why it matters: It solves the bandwidth bottleneck. By processing sensitive production data locally on the NPU, manufacturers achieve millisecond latency and enhanced privacy, eliminating the need to stream terabytes of raw video footage to the cloud.
2. Workload Consolidation via Virtualization

Factory floors have traditionally been cluttered with hardware: a PLC for control, an HMI for visualization, and a gateway for telemetry. The trend for 2026 is strictly “All-in-One.”
Thanks to the high core counts of modern embedded processors, engineers are now leveraging Hypervisor technology to run mixed-criticality workloads on a single rugged device.
- Real-world application: Imagine a single IPC running a Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) on two dedicated cores for motion control, while simultaneously running Windows 11 IoT on the remaining cores for the operator interface and cloud dashboarding.
- The Benefit: This drastically lowers the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), simplifies cabling complexity, and reduces failure points.
3. Connectivity Upgrades: Wi-Fi 7 and 5G RedCap

In 2026, wire-like reliability over wireless channels is finally becoming a reality. Two specific protocols are reshaping how hardware connects:
- Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be): This is the game-changer for autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and AGVs. With Multi-Link Operation (MLO), devices can send data across multiple frequency bands simultaneously. This ensures that even in interference-heavy warehouses, vehicles maintain a stable connection while roaming.
- 5G RedCap (Reduced Capability): Not every sensor needs the blistering speed of full 5G. RedCap is the “Goldilocks” standard for 2026—offering better speed than 4G, but with lower power consumption and cost than standard 5G. Expect to see RedCap-native gateways becoming the standard for dense sensor networks.
4. Modular Compute (SOM) as a Standard
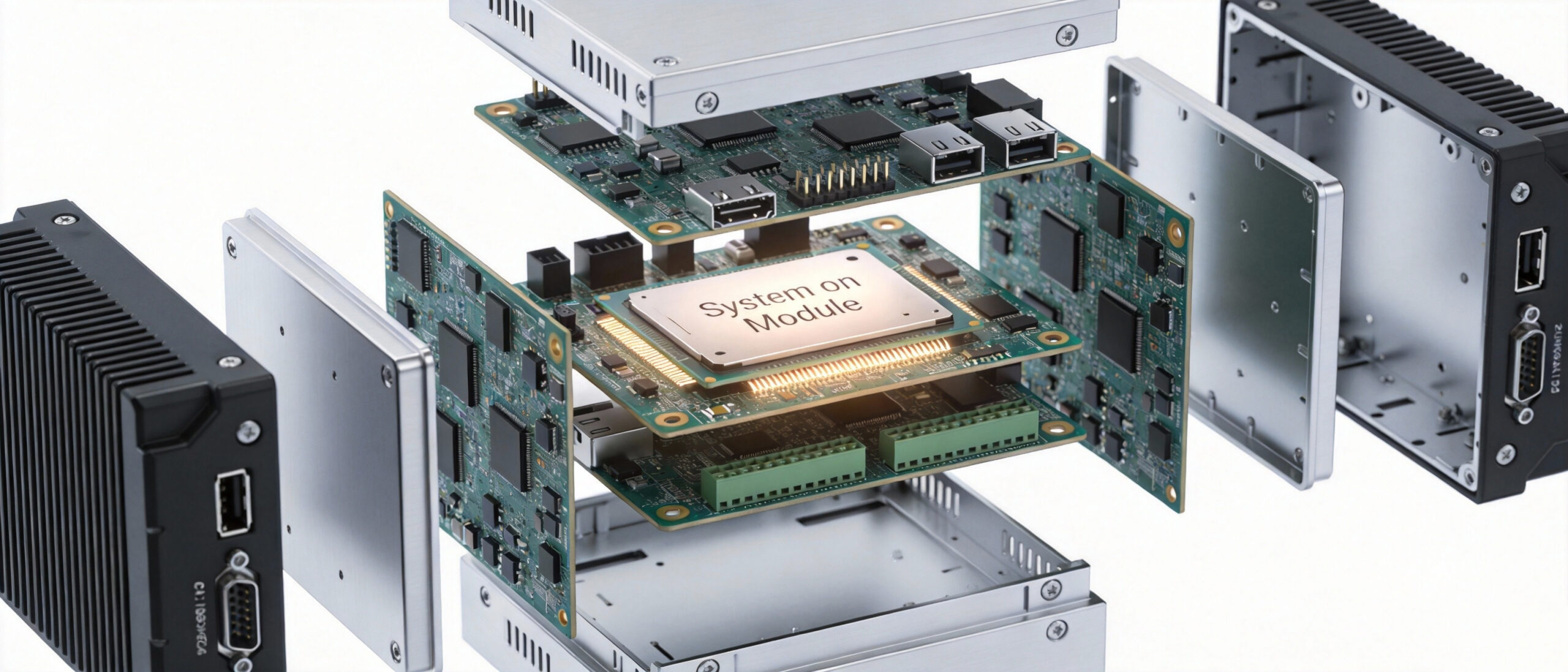
The pace of AI algorithm development is moving faster than the lifecycle of industrial machinery. To prevent hardware from becoming obsolete within two years, the industry is aggressively adopting System on Module (SOM) architectures.
Instead of soldering the processor to the mainboard, manufacturers are using modular compute units. If you need to upgrade from an entry-level AI model to a complex Large Language Model (LLM) at the edge in 2027, you won’t need to replace the entire industrial controller—just the compute module. This modularity is becoming a key requirement in RFQs (Requests for Quotation) this year.
5. Hardware-Enforced Zero Trust Security
Cybersecurity is no longer just a software concern. With the convergence of OT and IT, the attack surface has widened. In response, 2026 hardware is being built with a “Zero Trust” philosophy at the physical level.
We are seeing a mandate for TPM 2.0 modules and security processors like Microsoft Pluton becoming standard in industrial builds. Furthermore, compliance with IEC 62443-4-2 is becoming a baseline requirement. This ensures that the hardware itself—from the BIOS to the boot process—is hardened against tampering before the operating system even loads.
Final Thoughts: Future-Proofing Your 2026 Infrastructure
The industrial computing hardware of 2026 is defined by a balance of raw power and efficiency. It is smaller, smarter, and more integrated than ever before.
For decision-makers, the strategy is clear: stop procuring hardware that solves yesterday’s problems. Look for NPU-enabled, Wi-Fi 7-ready, and virtualization-capable devices. These are the pillars that will support the next generation of smart manufacturing.

HYSTOU
HYSTOU has established its R&D headquarters in Shenzhen, drawing on over a decade of experience. Our core team members, who previously served at renowned companies such as Inventec and Quanta Computer, form the backbone of our technical expertise. With robust R&D and innovation capabilities, we remain steadfast in our commitment to pursuing excellence in the field of technology products.





