How to Ensure 24/7 Reliability for Industrial Computers in Harsh Conditions?

Space-Saving Design and Portability
Compared to traditional desktop computers, the HYSTOU Business Mini PC occupies significantly less space. Whether placed in a remote home office or a studio, it solves space resource shortages, allowing for a more efficient arrangement of office supplies. Furthermore, its compact size enables easy portability, letting small businesses with remote teams flexibly arrange workspaces and empowering employees to work from various locations.
What Defines “Harsh Conditions”?
- Extreme Temperatures: Environments that fluctuate rapidly between freezing cold and scorching heat (e.g., outdoor kiosks or steel mills).
- Airborne Particulates: Factories filled with conductive metal shavings, sawdust, oil mist, or fine textile fibers.
- Physical Stress: Constant vibration (railway transport) or sudden shock impacts (heavy machinery).
- Power Instability: Dirty power, voltage spikes, and unstable currents caused by heavy equipment starting and stopping.
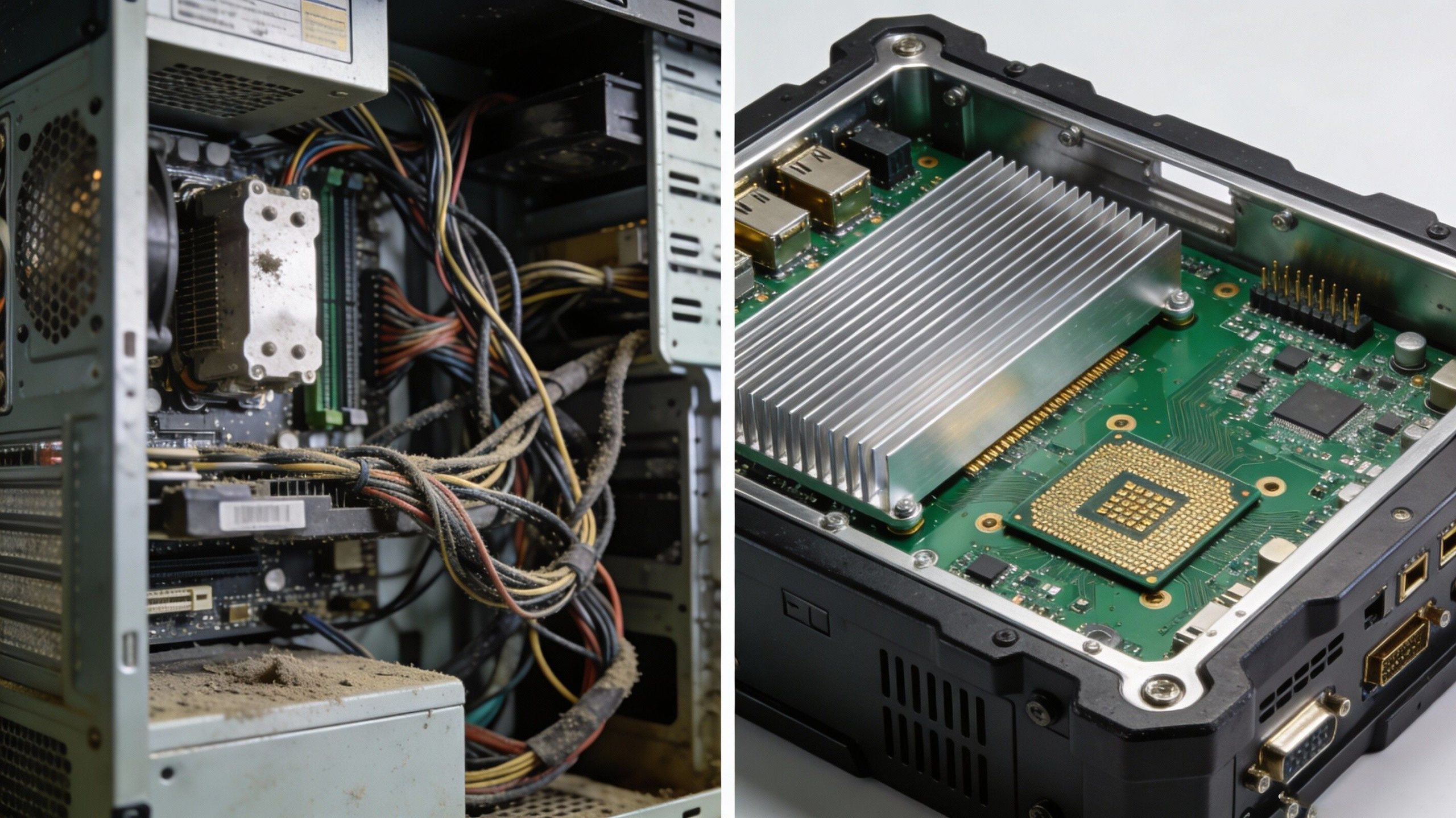
1. Eliminate Points of Failure: Fanless Design

To ensure 24/7 reliability, the industry standard is the Fanless Industrial Computer.
How It Works
- Heat Dissipation: The chassis itself (usually made of aluminum with fins) acts as a giant heat sink.
- Heat Pipes: Copper heat pipes transfer thermal energy from the CPU directly to the chassis surface.
The Reliability Benefit
2. Wide Temperature Tolerance
- The Standard: Look for computers rated for -40°C to 70°C (-40°F to 158°F).
- Under the Hood: This isn’t just about the CPU. Every capacitor, resistor, and memory module must be screened to ensure they don’t leak, crack, or lose capacitance during thermal cycling.
3. Shock and Vibration Resistance
- Cable-less Design: Top-tier industrial computers use board-to-board connections rather than internal wires. This eliminates the risk of cables wiggling loose due to vibration.
- Industrial SSDs: Never use spinning Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) in harsh environments. Industrial-grade Solid State Drives (SSDs) have no moving parts and offer superior data retention.
- Soldered Memory: In extreme vibration scenarios, verify if the RAM is soldered directly to the board (onboard RAM) rather than using standard DIMM slots.
Industry Standards You Should Check (MIL-STD, IP Ratings)

MIL-STD-810G
- What it proves: If a computer is MIL-STD-810G compliant (specifically Method 514.6 for vibration and 516.6 for shock), it has been lab-tested to survive drops and continuous shaking without failing.
IP Ratings (Ingress Protection)
- First Digit (Dust): 6 means “Dust Tight” (no dust can enter).
- Second Digit (Liquids): 5 means protection against water jets; 7 means protection against immersion.
- Selection Tip: For most factory floors, IP65 is the sweet spot—it protects against washdowns and dust without the high cost of full waterproof IP67/68 units.
4. Robust Power Protection
- Wide Voltage Input: Instead of a fixed 12V input, industrial PCs should accept a range (e.g., 9V–48V DC). This allows the system to keep running even if the voltage dips or surges.
- OVP/OCP: Over-Voltage and Over-Current Protection circuits are mandatory to prevent permanent hardware damage.
- Ignition Control: For vehicle-mounted computers, ignition control intelligence prevents the PC from draining the vehicle battery when the engine is off.
5. Autonomous Recovery: Watchdog Timers
- How it works: The WDT is a countdown timer on the motherboard. The software constantly resets this timer (indicating “I am alive”).
- The Safety Net: If the software freezes and fails to reset the timer, the WDT counts down to zero and automatically triggers a hardware reboot. This restores the system to operation within seconds, without human intervention.
Case Studies: Reliability in Action

- Problem: A textile manufacturer used standard tower PCs for line control. Cotton fibers clogged the fans weekly, leading to overheating and 4 hours of downtime per month.
- Solution: They switched to Fanless Industrial PCs with an IP65 rating. The sealed chassis prevented fiber ingress, resulting in zero hardware-related downtime over 24 months.
- Problem: Warehouse forklifts equipped with tablets faced constant data loss. The vibration from uneven floors caused the mechanical hard drives to fail.
- Solution: Deploying MIL-STD-810 G-certified computers with industrial SSDs and a cable-less internal design eliminated the disk failure issues, ensuring 24/7 inventory tracking.
FAQ: Common Questions on Industrial Computer Reliability
A: A consumer PC typically lasts 2-3 years. Industrial computers are designed for a long lifecycle, typically 5 to 7 years, with component support available for even longer to ensure consistency in your fleet.
A: Even in air-conditioned factories, dust is present. Fans are mechanical parts that will eventually fail (wear out). For mission-critical 24/7 applications, removing the fan eliminates a risk factor, regardless of temperature.
A: Don’t just look at the purchase price. Calculate TCO (Total Cost of Ownership):
TCO = Hardware Cost + (Cost of Downtime x Hours) + (Maintenance Labor) + (Replacement Frequency).
Usually, the industrial unit pays for itself after preventing just one significant downtime event.
Conclusion: Invest in Stability to Protect Your Bottom Line


HYSTOU
HYSTOU has established its R&D headquarters in Shenzhen, drawing on over a decade of experience. Our core team members, who previously served at renowned companies such as Inventec and Quanta Computer, form the backbone of our technical expertise. With robust R&D and innovation capabilities, we remain steadfast in our commitment to pursuing excellence in the field of technology products.





