BIOS RAID Setup: A Comprehensive Configuration Guide for 2025
When your server suddenly crashes due to a hard drive failure, have you ever wondered if there’s a way to protect your data while maintaining performance? The answer lies in BIOS RAID configuration—a critical skill for every IT professional in 2025. This guide will walk you through the entire process of setting up RAID through BIOS, from hardware preparation to performance verification, with real-world test data and expert insights to ensure you get it right the first time.
Prerequisites for BIOS RAID Configuration
Before diving into the setup process, you need to ensure your system meets these essential requirements:
- Motherboard Compatibility: Must support RAID configuration (check your motherboard manual or visit the manufacturer’s website for specifications).
- Storage Devices: Minimum 2 SATA SSD/HDD (including MSATA, M.2 SATA, or 2.5-inch SATA drives). For optimal performance, use drives with identical capacity and speed.
- Data Backup: All existing data on the drives will be erased during RAID setup. According to Backblaze’s 2025 Data Loss Report, 68% of RAID configuration failures result from inadequate backup procedures.
- UEFI Mode: After setup, the operating system must be installed in UEFI mode—legacy BIOS mode is not supported for RAID arrays.

Step-by-Step BIOS RAID Setup Process
Accessing BIOS Setup Utility
- Press the Del key rapidly after pressing the computer’s power button to enter BIOS Setup.
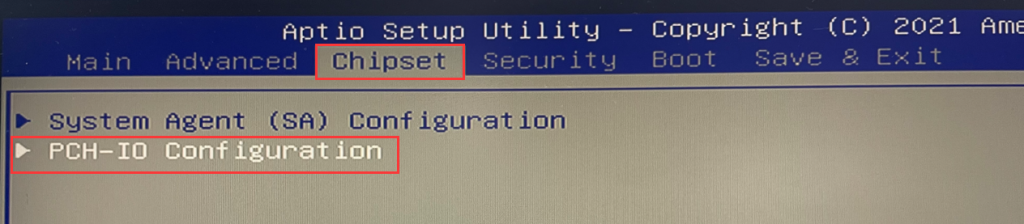
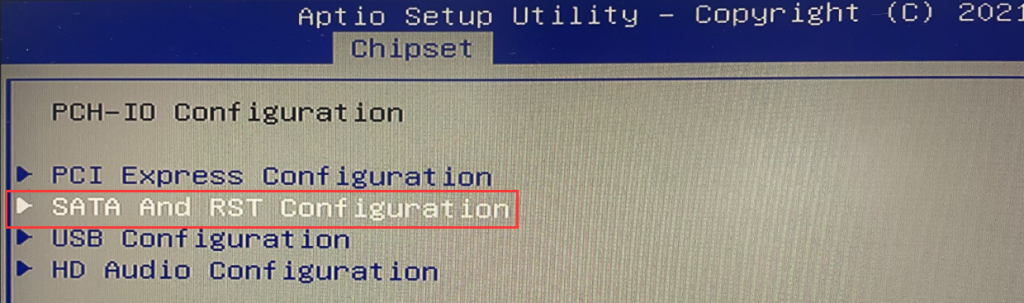
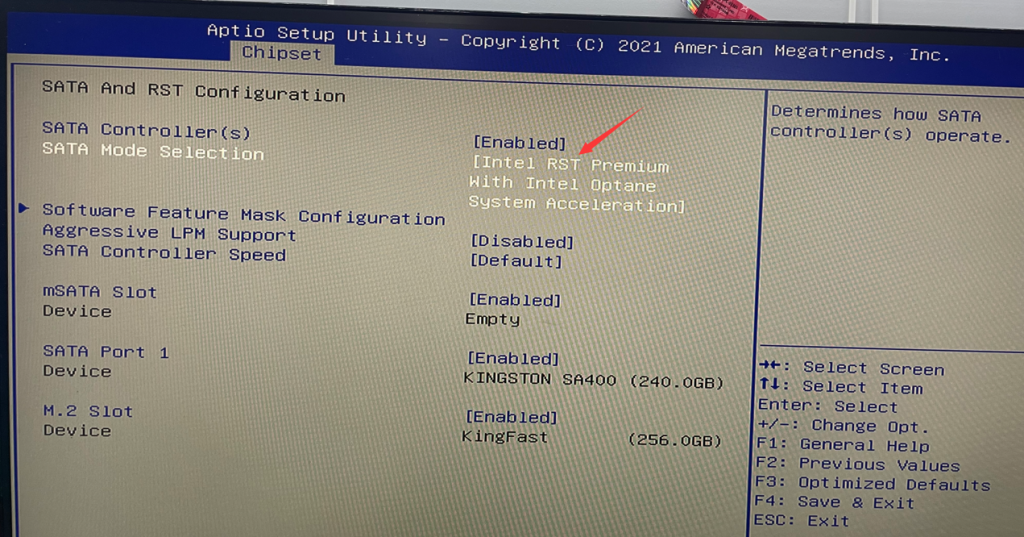
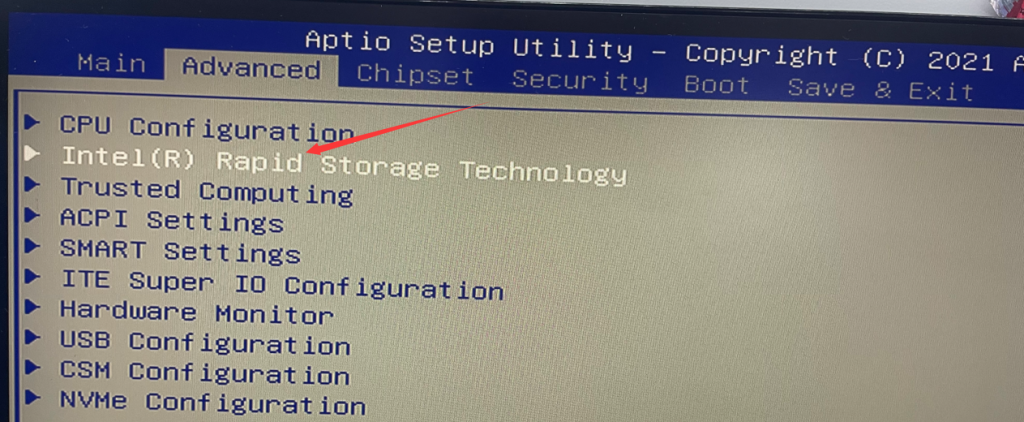
- In the BIOS, select Chipset > PCH-IO Configuration > SATA and RTS Configuration > Set the “SATA Mode Selection” to “Intel RST Premium with Intel Optane System Acceleration.” > Press the Esc key on the keyboard to exit the current page. Finally, select “Save & Exit.”
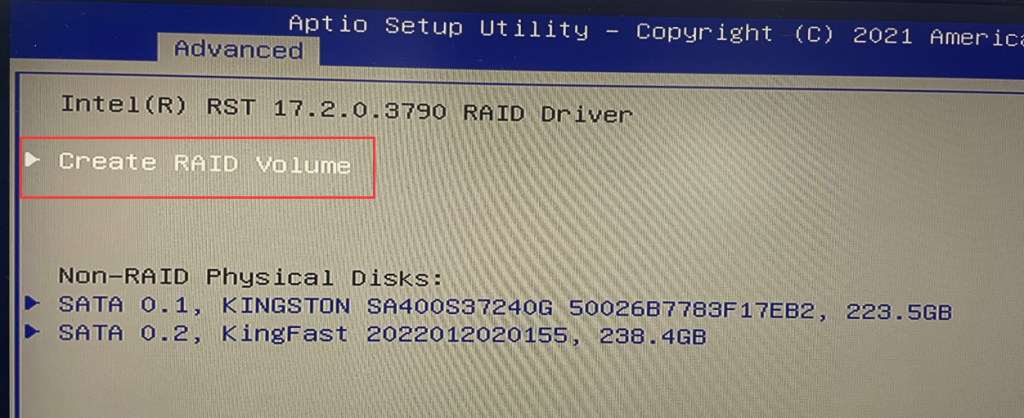
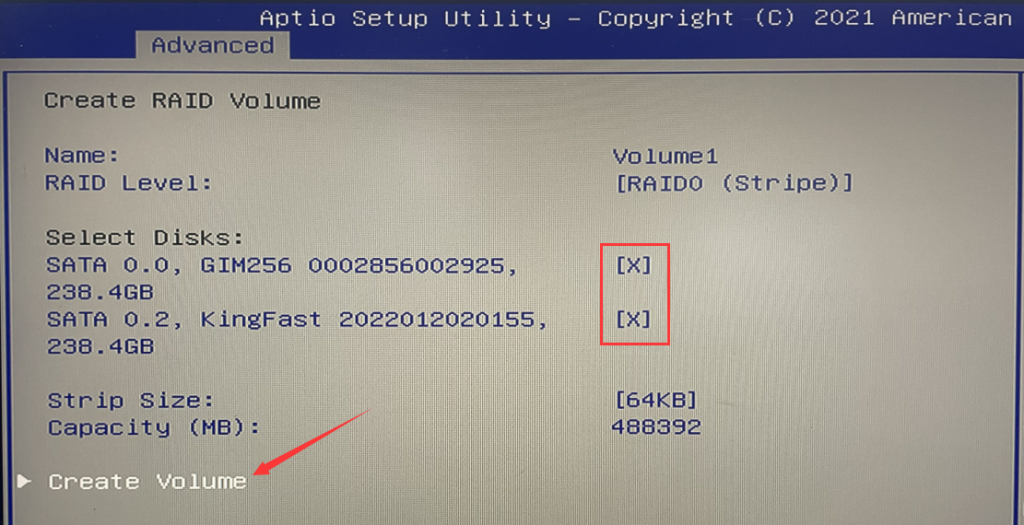
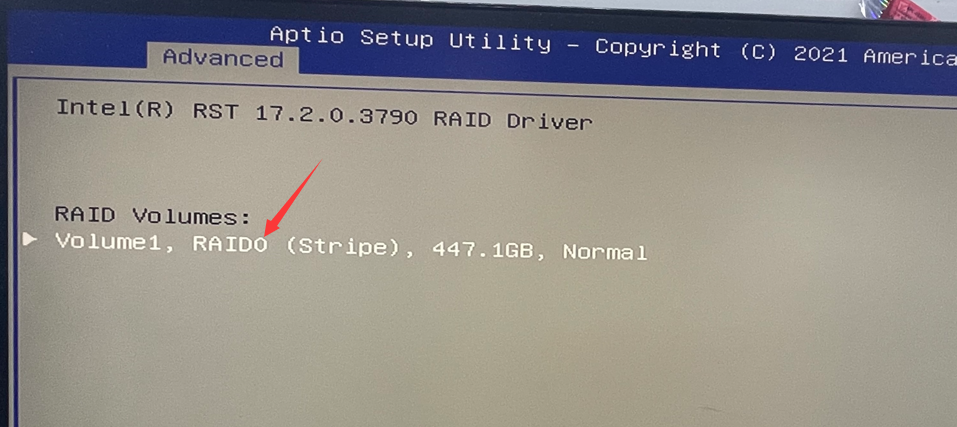
3. After restarting, quickly press the Del key to enter the BIOS. Select “Intel(R) Rapid Storage Technology” > “Create RAID Volume” > RAID level, such as RAID 0, RAID 1, or RAID 5 (Note: RAID requires at least three SATA hard drives for setup). In this tutorial, we will use RAID 0 as an example, but you can choose according to your needs. Select the disks by using the spacebar and then click “Create Volume.”
Conclusion: Making the Right RAID Choice for Your Needs
BIOS RAID configuration remains a cornerstone of data storage management in 2025, offering a perfect balance of performance and protection when implemented correctly. Remember:
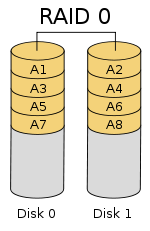
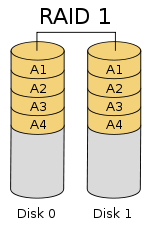
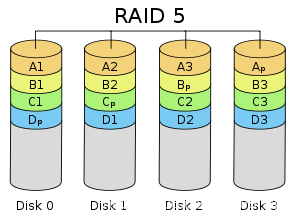
By following this guide and leveraging the included performance data, you’ll be able to configure a reliable RAID array that meets your specific needs while avoiding common pitfalls. As storage technology continues to evolve, staying current with BIOS RAID best practices will remain an essential skill for IT professionals worldwide.

HYSTOU
HYSTOU has established its R&D headquarters in Shenzhen, drawing on over a decade of experience. Our core team members, who previously served at renowned companies such as Inventec and Quanta Computer, form the backbone of our technical expertise. With robust R&D and innovation capabilities, we remain steadfast in our commitment to pursuing excellence in the field of technology products.





